Overview
The ThreatQ Data Exchange (TQX) allows the bi-directional sharing of threat intelligence across multiple ThreatQ instances. This allows your organization to build a centralized threat repository, referred to as a Publisher, that can transmit specific intel to various departments within your organization, known as Subscribers. These Subscribers can analyze the data they ingest and provide feedback to the Publisher via a new Data Feed.
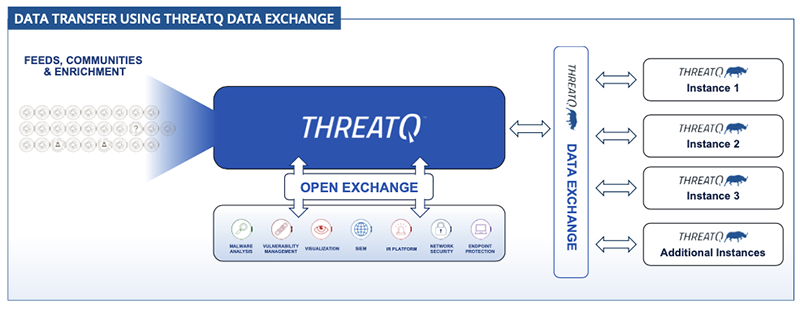
How it Works
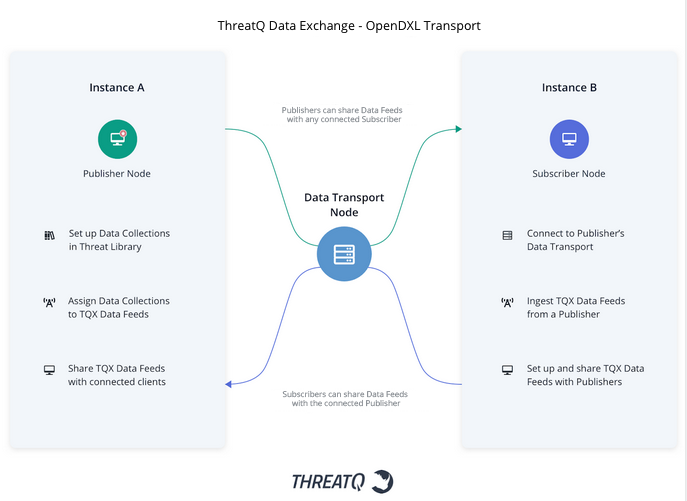
Instance Types
There are two different types of TQX instances available: Subscriber and Publisher.
Upgrading an instance to a Publisher license allows you to create Data Connection Bundles, which are used to create Data Connections with Subscribers. Once connected to a Subscriber, you can send and receive system objects in the form of Data Feeds. See the Publisher topic for further information.
You will need at least one Publisher instance in order to utilize TQX.
Upon upgrading to ThreatQ version 4.49+, your ThreatQ instance will have Subscriber permissions by default. As a Subscriber, you can connect to the data transport using the connection bundle sent to you by the Publisher and select the Data Feeds you want to receive as well as create Data Feeds and share them with the Publisher. See the Subscriber topic for further information.
Connection Bundles
Publishers can create connection bundles that allow Subscribers to connect via a data transport. This connection is a bi-directional connection between the Publisher and Subscriber and allows the sharing of data collections in the form of Data Feeds.
Publishers and Subscribers use a multi-step wizard to create their first connections. Additional connections are managed through your Topology View.
See the Getting Started - First Connections, Publisher, and Subscriber topics for further information.
Data Feeds
Users can create and edit Data Feeds that they wish to obtain specific data from in order to send information to others through the ThreatQ Data Exchange.
A Publisher can use a saved Data Collection from the ThreatQ Threat Library to create a Data Feed. That Data Feed can be offered to one or more recipients, which can be Subscribers or Publishers, for subscription. Once a recipient subscribes to the Data Feed, he receives data from it at a user-defined frequency.
A Publisher can send and receive Data Feeds to/from a Subscriber. A Subscriber can send and receive Data Feeds to/from a Publisher. A Subscriber cannot send Data Feeds to another Subscriber. Subscribers are not be able to see another Subscriber in their Topology View.
See the Data Feeds topic for further details.
Example - One Publisher, Two Subscribers
A Publisher creates a Data Feed, named Alpha, and assigns it to two connected Subscribers with a publish frequency set to hourly. When they subscribe to the Data Feed, both Subscribers will receive Data Feed Alpha's information every hour.
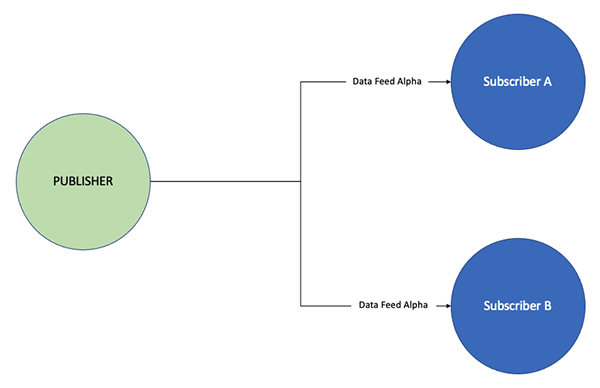
Example - One Publisher, Two Subscribers with Different Data Feeds
In this example, the Publisher is offering Data Feeds to two Subscribers. The Publisher selects one feed to be offered to Subscriber A and two feeds to be offered to Subscriber B. In this scenario, Subscriber A and B can subscribe to Data Feed Alpha. Additionally, Subscriber B also has the option to subscribe to a second Data Feed, Beta, from the Publisher.
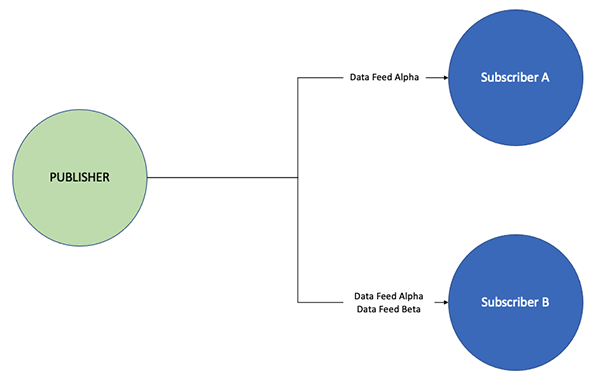
Example - One Publisher, Two Subscribers with a Subscriber Sending a Feed to the Publisher
In this example, in addition to subscribing a Data Feed from a Publisher, Subscriber A is also offering its own Data Feed back to the Publisher for subscription.
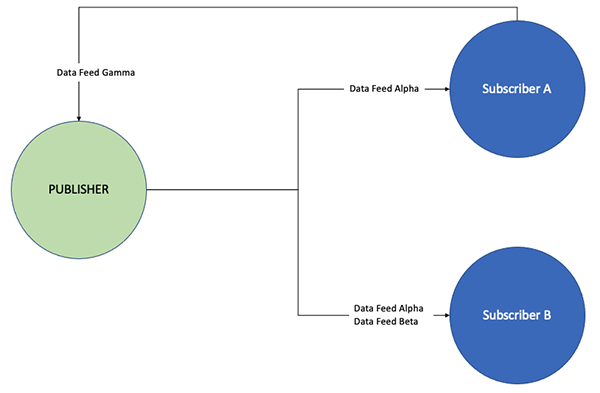
Managing Connections
Publishers and Subscribers can view connections, instance details, and activity logs via a node-based interface referred to as the Topology View.
Publishers can see all Subscribers that they are connected to in the Topology View. Subscribers only see their instance node and the Publisher(s) they are connected to in the view. Subscribers cannot see or submit/receive data from other Subscribers.
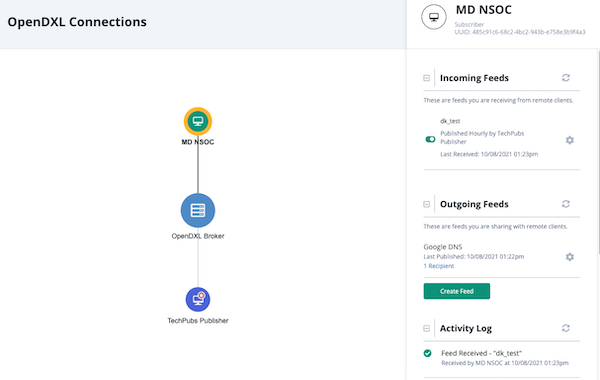
The view and available actions differ based on your instance type (Publisher, Subscriber). See the Publisher and Subscriber topics for more details.