ThreatQ ChatGPT Operation
The web format of this guide reflects the most current release. Guides for older iterations are available in PDF format.
Integration Details
ThreatQuotient provides the following details for this integration:
| Current Integration Version | 1.0.2 |
| Compatible with ThreatQ Versions | >= 5.22.0 |
| ChatGPT Versions | 3.5, 4.0 |
| Support Tier | ThreatQ Supported |
Introduction
The ThreatQ ChatGPT Operation queries ChatGPT for information on user-selected objects in the ThreatQ Threat Library.
The operation provides the following actions:
- Tool Query - queries ChatGPT for information on the tool object submitted.
- Adversary Query - queries ChatGPT for information on the adversary object submitted.
- Malware Query - queries ChatGPT for information on the malware object submitted.
The operation is able to work on the following object types:
- Malware
- Adversary
- Tool
Prerequisites
The operation requires an OpenAI API Key which can be generated at https://platform.openai.com/account/api-keys.
As of this publication, users can generate and use a 3.5 API account for free with limited use. ThreatQuotient recommends upgrading to a paid OpenAI account when deploying this operation into production.
Additional information regarding OpenAI Policy usage can be found at https://openai.com/policies/usage-policies.
Installation
This integration can be installed in the My Integration section of your ThreatQ instance. See the Adding an Integration topic for more details.
Configuration
ThreatQuotient does not issue API keys for third-party vendors. Contact the specific vendor to obtain API keys and other integration-related credentials.
To configure the integration:
- Navigate to your integrations management page in ThreatQ.
- Select the Operation option from the Type dropdown (optional).
- Click on the integration entry to open its details page.
- Enter the following parameter under the Configuration tab:
Parameter Description API Key API key to be used for the ChatGPT API ChatGPT Model Select the ChatGPT Model to use. Options include: - GPT-3.5-Turbo (default)
- GPT-4
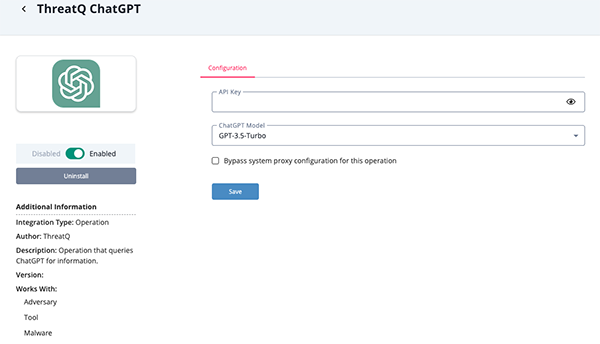
- Review any additional settings, make any changes if needed, and click on Save.
- Click on the toggle switch, located above the Additional Information section, to enable it.
Actions
The operation provides the following actions:
| Action | Description | Object Type | Object Subtype |
|---|---|---|---|
| Malware Query | Query the ChatGPT for malware information. | Malware | N/A |
| Adversary Query | Query the ChatGPT for adversary information. | Adversary | N/A |
| Tool Query | Query the ChatGPT for tool information. | Tool | N/A |
All actions share the same mapping table. The run parameters will differ based on the action.
Action Mapping
All actions query ChatGPT for information on the submitted object.
See the individual run parameters for what type of information can be retrieved for each object type.
{{ POST }} https://api.openai.com/v1/chat/completions
Sample Response:
{
'usage': {
'prompt_tokens': 20,
'completion_tokens': 536,
'total_tokens': 556
},
'object': 'chat.completion',
'choices': [
{
'message': {
'content': "To protect your organization from PowerNasa, a comprehensive strategy should include the following steps:\n\n1. Educate Employees: Train your employees about the risks associated with PowerNasa and other similar threats. Teach them about phishing emails, suspicious attachments, and the importance of not clicking on unknown links.\n\n2. Implement Strong Password Policies: Enforce strong password policies across your organization. Encourage employees to use unique, complex passwords and enable multi-factor authentication (MFA) wherever possible.\n\n3. Keep Software Up to Date: Regularly update all software, including operating systems, antivirus programs, and other security tools. This helps to patch any vulnerabilities that could be exploited by PowerNasa or other malware.\n\n4. Use Advanced Endpoint Protection: Deploy advanced endpoint protection solutions that can detect and block PowerNasa and other advanced threats. These solutions use machine learning and behavior analysis to identify and stop malicious activities.\n\n5. Secure Email Gateways: Implement secure email gateways that can filter out phishing emails and malicious attachments. These gateways can help prevent employees from falling victim to PowerNasa attacks delivered through email.\n\n6. Regularly Backup Data: Implement a robust backup strategy to ensure critical data is regularly backed up and stored securely. This helps to mitigate the impact of a PowerNasa attack or any other data loss event.\n\n7. Network Segmentation: Implement network segmentation to isolate critical systems and sensitive data from the rest of the network. This helps contain the spread of PowerNasa or other malware in case of a successful breach.\n\n8. Conduct Regular Security Audits: Perform regular security audits to identify any vulnerabilities or weaknesses in your organization's infrastructure. This includes penetration testing, vulnerability scanning, and code reviews.\n\n9. Employee Awareness Training: Conduct regular security awareness training sessions to keep employees updated on the latest threats, including PowerNasa. Teach them how to identify suspicious activities and report them to the IT department.\n\n10. Incident Response Plan: Develop a comprehensive incident response plan that outlines the steps to be taken in case of a PowerNasa attack or any other security incident. This plan should include procedures for containment, eradication, and recovery.\n\n11. Continuous Monitoring: Implement a robust security monitoring system that can detect and alert on any suspicious activities or anomalies. This helps in early detection and response to PowerNasa attacks.\n\n12. Engage a Cybersecurity Provider: Consider engaging a cybersecurity provider to assist with threat intelligence, incident response, and ongoing monitoring. They can provide expertise and resources to enhance your organization's security posture.\n\nRemember, cybersecurity is an ongoing process, and it is crucial to regularly review and update your strategy to adapt to evolving threats like PowerNasa.",
'role': 'assistant'
},
'finish_reason': 'stop',
'index': 0
}
],
'id': 'chatcmpl-8562MFzE1WPKRSTDTlxi04eJ1o9Q7',
'created': 1696225538,
'model': 'gpt-3.5-turbo-0613'
}ThreatQuotient provides the following default mapping for all actions:
| Feed Data Path | ThreatQ Entity | ThreatQ Object Type or Attribute Key | Published Date | Examples | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| choices[].message.content | Attribute | ChatGPT Response | N/A | To protect your organization from PowerNasa, a comprehensive ... | N/A |
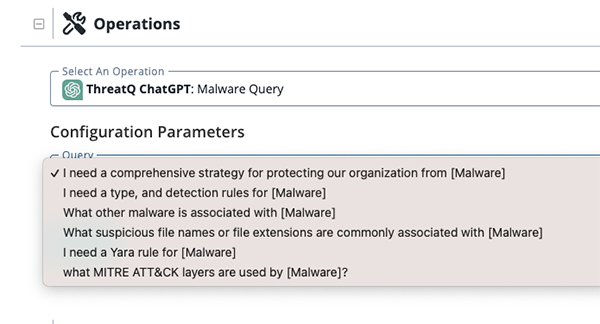
Malware Query Run Parameters
The Malware Query action provides the following parameter:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Query | The following options are available:
|
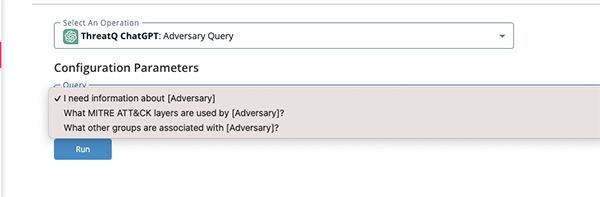
Adversary Query Run Parameters
The Adversary Query action provides the following parameter:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Query | The following options are available:
|
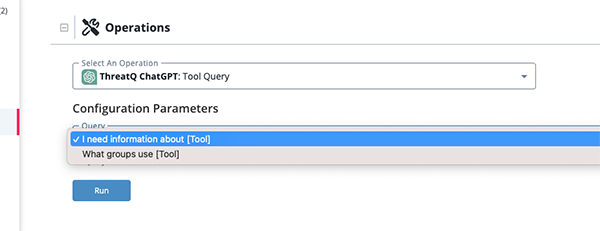
Tool Query Run Parameters
The Tool Query action provides the following parameter:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Query | The following options are available:
|
Known Issues / Limitations
-
Due to operation limitations, descriptions are updated with each run and subsequent ChatGTP response. Future planned updates for the operation will include an update so that each response will be ingested as a new description.
Change Log
- Version 1.0.2
- Added compatibility with GPT-4.
- Added new configuration option: ChatGPT Model. This allows you to select which GPT module to use with the operation.
- Updated the Known Issues / Limitations chapter of the guide in regards to descriptions.
- Updated minimum ThreatQ version to 5.22.0.
- Version 1.0.1
- Updated the operation's description in the ThreatQ UI.
- Version 1.0.0
- Initial release
PDF Guides
| Document | ThreatQ Version |
|---|---|
| ThreatQ ChatGPT Operation v1.0.2 | 5.22 or Greater |
| ThreatQ ChatGPT Operation v1.0.1 | 5.6 or Greater |
| ThreatQ ChatGPT Operation v1.0.0 | 5.6 or Greater |