HBase
The web format of this guide reflects the most current release. Guides for older iterations are available in PDF format.
Integration Details
ThreatQuotient provides the following details for this integration:
| Current Integration Version | 1.0.0 |
| Compatible with ThreatQ Versions | >= 4.30.0 |
| Support Tier | ThreatQ Supported |
Introduction
The ThreatQ Integration with HBase integration fetches indicators from a ThreatQ instance and ingests them into an HBase table.
Deployment Prerequisites
The following personnel and dependencies have been identified to ensure for a smooth deployment of the agreed-upon products and/or services.
Networking
- All required firewall rules are applied to allow for communications to, from, or between the applicable products, services, and/or API endpoints. Specifically:
- Ports are opened and firewall rules configured between ThreatQ and NiFi
- Ports are opened and firewall rules configured for communication among all applications in the Hadoop cluster
- At a minimum all ports listed in these documents should be opened in a Cloudera Hadoop deployment:
- Network access control modifications, proxy and firewall configurations to allow for the necessary communications between internal and external tools and data feeds
- If applicable, the customer will inform ThreatQuotient of any custom network configurations that would require modification(s) to the standard ThreatQ configuration to include, but not limited to:
- DNS resolution
- Proxy configuration
- Routing tables
Hardware/Software/Virtual Appliance(s)
- All ThreatQuotient equipment/virtual appliances are provisioned, online, and in service
- All third-party products and/or services are installed, configured, and operating normally
- If ThreatQ is already installed:
- ThreatQuotient engineers will require the username/password for command line root access to the appliance via SSH port 22.
- ThreatQuotient engineers will require the username/password for the maintenance account in order to access the appliance via the UI.
ThreatQ
Install a Signed Certificate
The ThreatQ virtual appliance is supplied with a self-signed certificate, which is not trusted by NiFi, and as such NiFi will not initiate traffic from ThreatQ. In order for the ingestion process to work, the customer will need to install a CA-signed certificate on ThreatQ.
Create a ThreatQ Export
For the detailed steps on how to create an export in ThreatQ, please visit this Helpcenter topic, and scroll to Adding an Export: https://helpcenter.threatq.com/index.htm#t=ThreatQ_Platform%2FExports%2FManaging_Exports.htm.
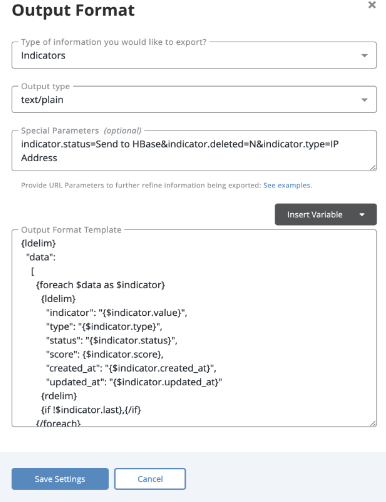
- Use the following values to fill out the export template:
Field Description Type of information you would like to export? Indicators Output Type Text/Plain Special Parameters indicator.status=Send to HBase&indicator.deleted=N&indicator.type=IPAddressOutput Format Template
{ldelim} "data": [ {foreach $data as $indicator} {ldelim} "indicator": "{$indicator.value}", "type": "{$indicator.type}", "status": "{$indicator.status}", "score": {$indicator.score}, "created_at": "{$indicator.created_at}", "updated_at": "{$indicator.updated_at}" {rdelim} {if !$indicator.last},{/if} {/foreach} ] {rdelim - Click on Save Settings, and when completed, is should look similar to the snapshot below.
- Click on the generated Export URL. This will execute the export process in the backend and will list all the indicators that match the export’s special parameters.
- Copy the URL and paste it in the URL value in the GetHTTP processor in NiFi.
NiFi
This section discusses the prerequisites for NiFi.
Import XML Template
- Navigate to the NiFi UI. On the instruments menu, click on the right-most button Upload Template.
- Next, click on the magnifying glass to the right of Select Template. This will open the window that will allow you to navigate to the XML template to import.
Add Template to the Canvas
To add the template to your canvas:
- Go to the NiFi UI, and drag a Template from the instruments onto the canvas.
This will open a modal window with a dropdown from which you can choose the template that was just imported.
- Select the template threatq-hbase-integration-<version> which will be used for ingesting threat intel from ThreatQ into HBase.

JVM Heap Maximum
The default memory allocation for NiFi is 512MB, which needs to be increased to at least 4GB, but the recommended is 8GB.
To increase it:
- Navigate to Ambari.
- Click on the NiFi application, and then click on Configs for NiFi.
- Search for “Max memory allocation”, as shown in the snapshot below.
- Change the value to 8192m and save it.
After the changes are made, Ambari will prompt you to restart all the NiFi services. - Click on restart and wait for the application to restart. After the restart is complete, validate the amount of resources used by NiFi.
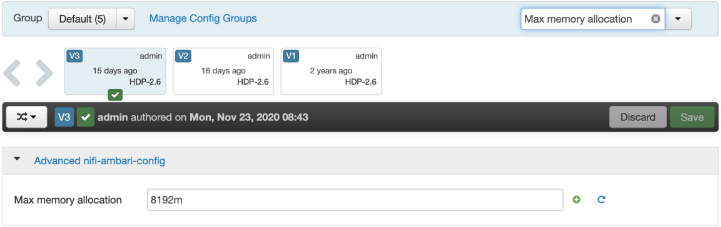
In Ambari-managed Hadoop clusters, this can be done by navigating to the NiFi UI, click on the hamburger menu in the upper right corner, and then click on the Cluster settings.
On the NiFi resources, navigate to the JVM tab, which shows the Java heap usage.
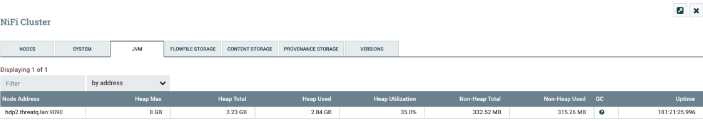
This is also a good way to determine the optimal memory needed for NiFi. Run the NiFi flow multiple times with different loads, and make sure that the Heap Utilization metric on the JVM tab stays below 70%. That leaves a buffer to handle occasional flows with peak memory demand.
User Permissions
NiFi runs as the user specified in the bootstrap.conf file, the content of which is accessible via Ambari. This user should have the proper permissions to:
- Parse the NetFlow files with nfdump
- Write to HDFS
- Publish to Kafka topics
- Perform lookups against HBase
Perform the following steps if you need to change the user:
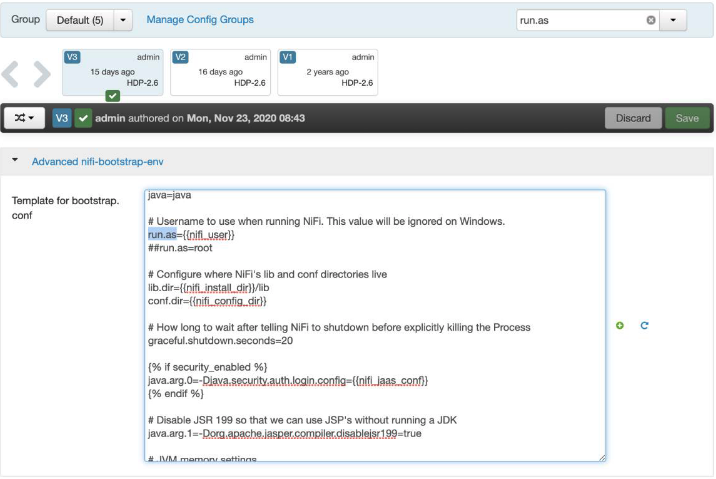
- Navigate to the NiFi configuration in Ambari.
- Enter run.as in the search. This should bring up the content of the bootstrap.conf file.
- Make the required changes and restart all the services Ambari lists. In the example below, NiFi runs as the “nifi” user.
NiFi Flow Configuration
The following sections details the configuration of each processors in the NiFi flow that ingests indicators from ThreatQ, parses and writes them to an HBase table. The flow has also been provided separately as an XML file to import into NiFi.
Fetch Indicators from ThreatQ
- Select the GetHTTP processor, and configure it as shown below.
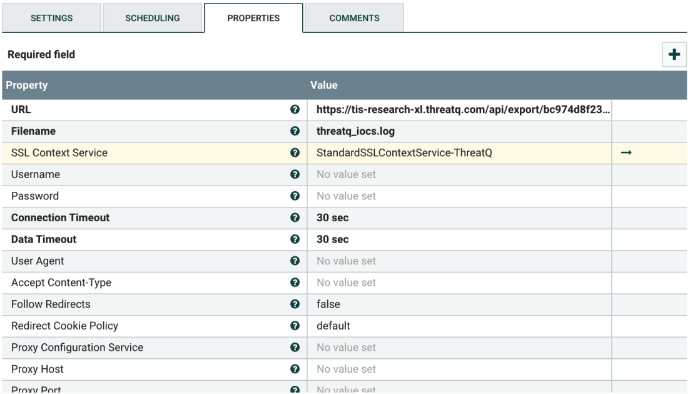
ThreatQ needs to have a CA-signed certificate in order for this to work, because NiFi checks the certificate.
- Change the following value:
Value Description URL Change the value to the URL your ThreatQ instance has generated. - Select the StandardSSLContextService for the SSL Context Service property.
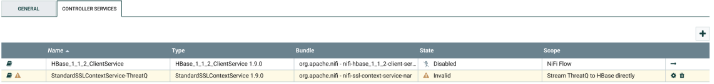
- Click on the arrow to the right, which will bring you to the NiFi Flow Configuration screen.
- Click on the wheel for the StandardSSLContextService on the NiFi Flow Configuration screen.
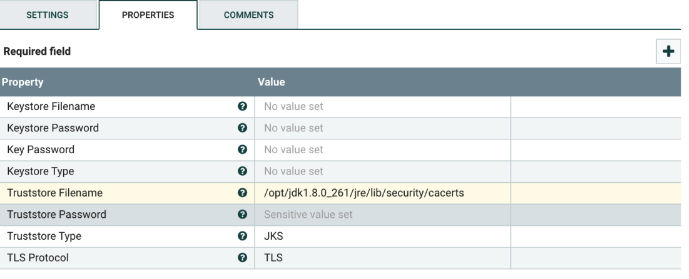
- After the controller details open, configure it as shown below, and enable it by clicking on the lightning bolt.
For Truststore Password use
changeit.Value Description Truststore File Name Change the path to the Truststore in your environment. Truststore Password The default password is changeit. If ou have changed it, use the new one.
Split the JSON array into separate documents
Select the SplitJson processor, and configure it as shown below. Below is the minimum list of properties that needs to be configured.
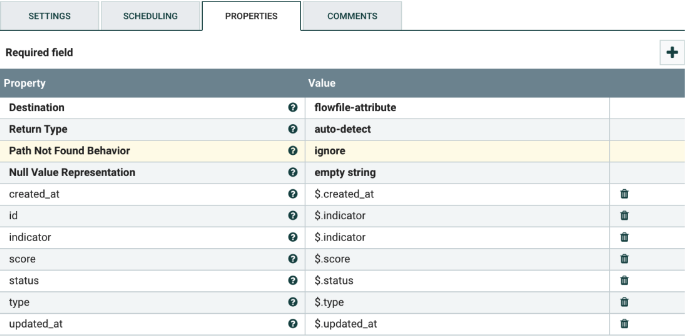
Parse the data into JSON
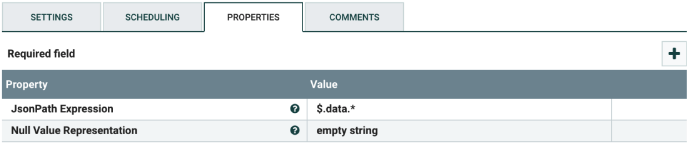
Select the EvaluateJsonPath processor, and configure it as shown below. Below is the minimum list of properties that needs to be configured. There is no need to change any of the values in the template for the processor, unless more fields are added in the ThreatQ export.
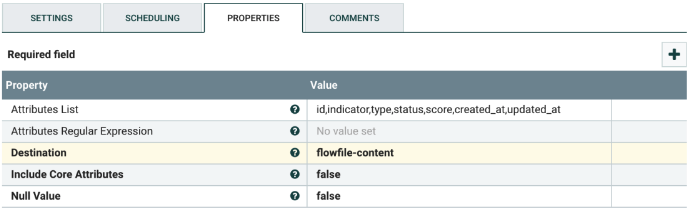
Convert attributes to JSON
Select the AttributesToJSON processor, and configure it as shown below. Below is the minimum list of properties that needs to be configured. There is no need to change any of the values in the template for the processor, unless more fields are added in the ThreatQ export. If more fields are added, add their names to the Attributes List in the processor.
Put JSON Documents into HBase Table
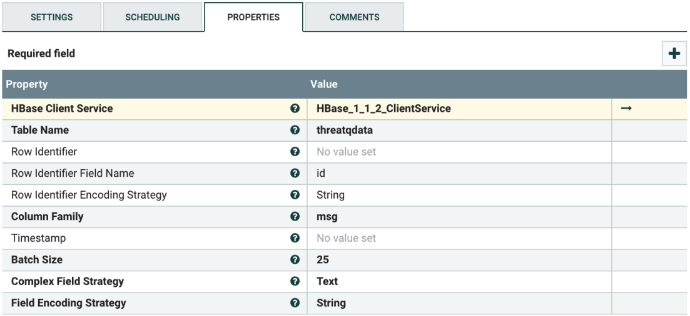
- Select the PutHBaseJSON processor and configure the minimum list of properties that needs to be configured.
Value Description Table Name The name of the table to which the threat intel is stored in HBase. Column Family Column family in the threat intel HBase table. Your screen should resemble the screenshot example below.
- Click on the wheel for the HBase_1_1_2_ClientService on the NiFi Flow Configuration screen. After the controller details opens, configure it as shown below, and enable it by clicking on the lightning bolt.
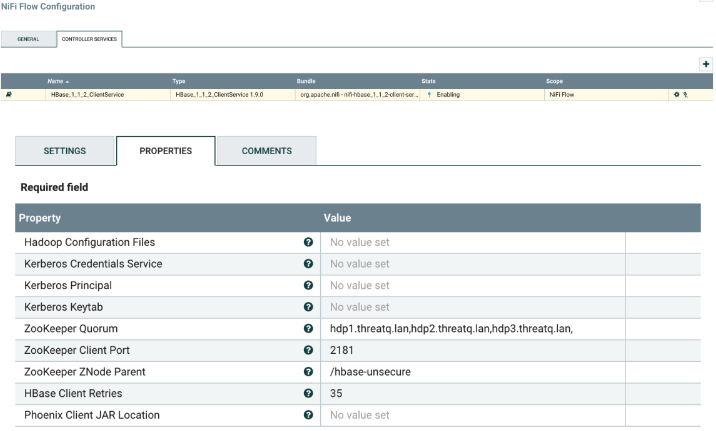
This controller requires the HBase configuration details. There are two options for the configuration:Option 1
Fill out the value for Hadoop Configuration Files with comma-separated list of Hadoop configuration file paths, such as hbase-site.xml, and core-site.xml for Kerberos, including full paths to the files. The configuration files should be located in a local path on the NiFi instance or mounted to a drive NiFi can read from.
Example: "/usr/local/hbase/conf/hbase-site.xml,/usr/local/hbase/conf/core- site.xml"
Option 2
Get the config details from the HBase config file hbase-site.xml which is usually located somewhere on the host that has HBase installed. Get the following details from that file and fill them out in the controller window:
Field Description Zookeeper Quorum Comma-separated list of the Zookeeper hosts (from hbase- site.xml). Zookeeper Client Port The port Zookeeper is listening on (from hbase-site.xml). Zookeeper ZNode Parent Zookeeper ZNode Parent (from hbase-site.xml). HBase Client Retries HBase retries (from hbase-site.xml).
Change Log
- Version 1.0.0
- Initial release
PDF Guides
| Document | ThreatQ Version |
|---|---|
| HBase Integration Guide v1.0.0 | 4.30.0 or Greater |