Trellix ESM Connector
The web format of this guide reflects the most current release. Guides for older iterations are available in PDF format.
Integration Details
ThreatQuotient provides the following details for this integration:
| Current Integration Version | 1.0.0 |
| Compatible with ThreatQ Versions | >= 5.6.0 |
| Python Version | 3.6 |
| Support Tier | ThreatQ Supported |
Introduction
ThreatQ v6 Users – while the connector’s overall operation remains the same, installation and usage commands for ThreatQ v6 users will differ from what is listed in this guide. See the Installing Custom Connectors in ThreatQ v6 and Installing Custom Connectors on Another Instance topics for additional information.
The Trellix ESM connector interacts with the Trellix ESM server.
The integration uses the Trellix ESM API to upload indicators to watchlists based on at least one user-defined saved ThreatQ Threat Library search. These searches are used to keep the data within the Trellix ESM watchlists fresh, and it ages out stale data with every execution.
The integration also polls for Alarms that have names starting with ThreatQ. These alarms are brought over as Sighting type events in ThreatQ. This provides feedback to the threat analysts working with ThreatQ, giving them information on sightings of IoCs within the customer environment.
Prerequisites
Review the following requirements before attempting to install the connector.
Third-Party Credentials
Trellix ESM hostname and credentials.
Time Zone
The time zone steps are for ThreatQ v5 only. ThreatQ v6 users should skip these steps.
You should ensure all ThreatQ devices are set to the correct time, time zone, and date (UTC is recommended), and using a clock source available to all.
To identify which time zone is closest to your present location, use the timedatectl command with the list-timezones command line option.
For example, enter the following command to list all available time zones in Europe:
timedatectl list-timezones | grep Europe Europe/Amsterdam Europe/Athens Europe/Belgrade Europe/Berlin
Enter the following command, as root, to change the time zone to UTC:
timedatectl set-timezone UTC
Integration Dependencies
The integration must be installed in a python 3.6 environment.
The following is a list of required dependencies for the integration. These dependencies are downloaded and installed during the installation process. If you are an Air Gapped Data Sync (AGDS) user, or run an instance that cannot connect to network services outside of your infrastructure, you will need to download and install these dependencies separately as the integration will not be able to download them during the install process.
Items listed in bold are pinned to a specific version. In these cases, you should download the version specified to ensure proper function of the integration.
| Dependency | Version | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| threatqsdk | >=1.8.7 | N/A |
| threatqcc | >=1.4.2 | N/A |
| tqTaxiiExport | >=2.1.1 | N/A |
| ruamel.yaml | >=0.17.26 | N/A |
| ipaddress | N/A | N/A |
| requests | N/A | N/A |
Installation
The following provides you with steps on installing a Python 3 Virtual Environment and installing the connector.
Creating a Python 3.6 Virtual Environment
Run the following commands to create the virtual environment:
mkdir /opt/tqvenv/
sudo yum install -y python36 python36-libs python36-devel python36-pip
python3.6 -m venv /opt/tqvenv/<environment_name>
source /opt/tqvenv/<environment_name>/bin/activate
pip install --upgrade pip
pip install threatqsdk threatqcc
pip install setuptools==59.6.0
Proceed to Installing the Connector.
Installing the Connector
Upgrading Users - Review the Change Log for updates to configuration parameters before updating. If there are changes to the configuration file (new/removed parameters), you must first delete the previous version's configuration file before proceeding with the install steps listed below. Failure to delete the previous configuration file will result in the connector failing.
- Navigate to the ThreatQ Marketplace and download the .whl file for the integration.
- Activate the virtual environment if you haven't already:
source /opt/tqvenv/<environment_name>/bin/activate
- Transfer the whl file to the
/tmpdirectory on your ThreatQ instance. - Install the connector on your ThreatQ instance:
pip install /tmp/tq_conn_trellix_esm-<version>-py3-none-any.whl
A driver called
tq-trellix-esmwill be installed. After installing, a script stub will appear in/opt/tqvenv/<environment_name>/bin/tq-trellix-esm. - Once the application has been installed, a directory structure must be created for all configuration, logs and files, using the
mkdir -pcommand. Use the commands below to create the required directories:mkdir -p /etc/tq_labs/
mkdir -p /var/log/tq_labs/ - Perform an initial run using the following command:
/opt/tqvenv/<environment_name>/bin/tq-trellix-esm -ll /var/log/tq_labs/ -c /etc/tq_labs/ -v3
- Enter the following parameters when prompted:
Parameter Description ThreatQ Host This is the host of the ThreatQ instance, either the IP Address or Hostname as resolvable by ThreatQ. ThreatQ Client ID This is the OAuth id that can be found at Settings Gear → User Management → API details within the user’s details. ThreatQ Username This is the Email Address of the user in the ThreatQ System for integrations. ThreatQ Password The password for the above ThreatQ account. Example Output
/opt/tqvenv/<environment_name>/bin/tq-trellix-esm -ll /var/log/tq_labs/ -c /etc/tq_labs/ -v3 ThreatQ Host: <ThreatQ Host IP or Hostname> ThreatQ Client ID: <ClientID> ThreatQ Username: <EMAIL ADDRESS> ThreatQ Password: <PASSWORD> Status: Review Connector configured. Set information in UI
You will still need to configure and then enable the connector.
Configuration
ThreatQuotient does not issue API keys for third-party vendors. Contact the specific vendor to obtain API keys and other integration-related credentials.
To configure the integration:
- Navigate to your integrations management page in ThreatQ.
- Select the Labs option from the Category dropdown (optional).
- Click on the integration entry to open its details page.
- Enter the following parameters under the Configuration tab:
Parameter Description Trellix ESM Hostname This is the hostname or IP address of the Trellix ESM instance. Trellix ESM Username This is a Trellix ESM User that has access to the API. We suggest to make a separate user for this purpose. This user should have the capability to add, delete, and edit a watchlist. Trellix ESM Password This is the password for the user above. Trellix ESM Configuration This is a YAML-formatted configuration field, described in the Trellix ESM Configuration section below. A default template value is provided. 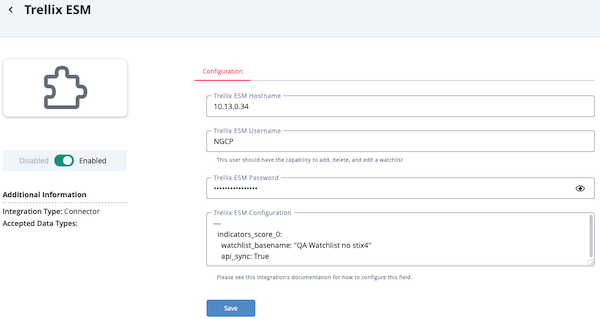
- Review any additional settings, make any changes if needed, and click on Save.
- Click on the toggle switch, located above the Additional Information section, to enable it.
Trellix ESM Configuration Field
The Trellix ESM Configuration field is YAML-formatted. This field maps data from saved ThreatQ Threat Library searches to watchlists within Trellix ESM. The default template value of the configuration is:
---
<Saved ThreatQ Threat Library Search Name>:
watchlist_basename: "Trellix ESM Watchlist Basename"
api_sync: TrueThe value <Saved ThreatQ Threat Library Search Name> is the name of a saved ThreatQ Threat Library search. (multiple searches can be configured)
watchlists_basename determines the basename of the six watchlists (one for each indicator type) that will be created on the ESM machine.
api_sync determines if the watchlist synchronization should be done by using the REST API (if True) or through the ESM Cyber Threat Feeds (if False)
Usage
Use the following command to execute the driver:
/opt/tqvenv/<environment_name>/bin/tq-trellix-esm -v3 -ll /var/log/tq_labs/ -c /etc/tq_labs/
Command Line Arguments
This connector supports the following custom command line arguments:
| Argument | Description |
|---|---|
-h, --help |
Review all additional options and their descriptions. |
-ll LOGLOCATION, --loglocation LOGLOCATION |
Sets the logging location for the connector. The location should exist and be writable by the current. A special value of 'stdout' means to log to the console (this happens by default). |
-c CONFIG, --config CONFIG |
This is the location of the configuration file for the connector. This location must be readable and writable by the current user. If no config file path is given, the current directory will be used. This file is also where some information from each run of the connector may be put (last run time, private oauth, etc.) |
-v {1,2,3}, --verbosity {1,2,3} |
This is the logging verbosity level where 3 means everything. |
-n, --name |
Optional - Name of the connector (Option used in order to allow users to configure multiple connector instances on the same TQ box). |
-hist, --historical {DATE} |
Optional - Allows you to set the start date for the Threat Library search. |
-lc |
Optional - The locale required by Trellix ESM API during connection. This will default to "en_US". |
Cyber Threat Feeds
If using Cyber Threat Feeds (api_sync is set to False), indicators are written to a STIX 1.1.1 XML file on the TQ box (at /home/mcesm/<watchlist_basename>/iocs.stix) instead of being transferred to the ESM machine via ESM's REST API. ESM will eventually fetch these created STIX files in order to populate its watchlists with indicators.
In order to use and configure the Cyber Threat Feeds feature, the Linux user mcesm needs to be manually created on the TQ box by running:
useradd mcesm sudo passwd mcesm # Set a password for the new user
Basic Example
---
High Score Indicators:
watchlist_basename: "ThreatQ High Score Watchlist"
api_sync: True
Low Score Indicators:
watchlist_basename: "ThreatQ Low Score Watchlist"
api_sync: False
The above will take the indicators found by the ThreatQ Threat Library search named High Score Indicators, split them by IoC type, create the watchlists defined below in Trellix ESM, and upload the indicators through the REST API.
- ThreatQ High Score Watchlist - FQDN
- ThreatQ High Score Watchlist - IP Address
- ThreatQ High Score Watchlist - Email Address
- ThreatQ High Score Watchlist - URL
- ThreatQ High Score Watchlist - MD5
- ThreatQ High Score Watchlist - SHA1
The same process occurs for the ThreatQ Threat Library search named Low Score Indicators the only difference is that the indicators are not uploaded using the REST API, but instead a STIX file is created on the TQ box which will be fetched by the EMS machine through SCP by using the Cyber Threat Feeds feature.
Alarms
The purpose of this command is to download Alarms from Trellix ESM and create Sighting events in ThreatQ. This feedback loop of information from Trellix ESM will enable analysts to determine which indicators are being seen, what feeds those indicators originated from, and common attributes that these indicators may have. This information can help tune the advanced search used to fill the Trellix ESM watchlists.
During the execution of tq-trellix-get-alarms, alarms starting in ThreatQ more recent than the previous execution are downloaded. Information about these alarms are then downloaded and a Sighting event with a source of tq_trellix_esm is created. Indicators of compromise that are related to this alarm are created and linked against the event.
The reasoning behind requiring an alarm name to start with ThreatQ is that this provides the ability to select which Alarms are exported and provides an "at a glance" way to determine whether an Alarm is being exported to ThreatQ.
There will be a delay between the time when an alarm is reported in Trellix ESM and when that alarm's event will be listed in ThreatQ. This delay is determined by how often the tq-trellix-get-alarms command executes.
CRON
Automatic CRON configuration has been removed from this script. To run this script on a recurring basis, use CRON or some other jobs scheduler. The argument in the CRON script must specify the config and log locations.
Add an entry to your Linux crontab to execute the connector at a recurring interval. Depending on how quickly you need updates, this can be run multiple times a day (no more than once an hour) or a few times a week.
In the example below, the command will execute the connector every two hours.
- Log into your ThreatQ host via a CLI terminal session.
- Enter the following command:
crontab -e
This will enable the editing of the crontab, using vi. Depending on how often you wish the cronjob to run, you will need to adjust the time to suit the environment.
- Enter the commands below:
Every 2 Hours Example
0 */2 * * * /opt/tqvenv/<environment_name>/bin/tq-trellix-esm -c /etc/tq_labs/ -ll /var/log/tq_labs/ -v3
- Save and exit CRON.
Change Log
- Version 1.0.0
- Initial release
PDF Guides
| Document | ThreatQ Version |
|---|---|
| Trellix ESM Connector Guide v1.0.0 | 5.6.0 or Greater |